Rexroth

Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps are used in hydraulic drive systems and can be hydrostatic or hydrodynamic. A hydraulic pump is a mechanical source of power that converts mechanical power into hydraulic energy (hydrostatic energy i.e. flow, pressure). It generates flow with enough power to overcome pressure induced by the load at the pump outlet. When a hydraulic pump operates, it creates a vacuum at the pump inlet, which forces liquid from the reservoir into the inlet line to the pump and by mechanical action delivers this liquid to the pump outlet and forces it into the hydraulic system. Hydrostatic pumps are positive displacement pumps while hydrodynamic pumps can be fixed displacement pumps, in which the displacement (flow through the pump per rotation of the pump) cannot be adjusted, or variable displacement pumps, which have a more complicated construction that allows the displacement to be adjusted. Hydrodynamic pumps are more frequent in day-to-day life. Hydrostatic pumps of various types all work on the principle of Pascal's law.

Electronic Drive Controls
A hydraulic drive system is a quasi-hydrostatic drive or transmission system that uses pressurized hydraulic fluid to power hydraulic machinery. The term hydrostatic refers to the transfer of energy from pressure differences, not from the kinetic energy of the flow. A hydraulic drive system consists of three parts: The generator (e.g. a hydraulic pump), driven by an electric motor or a combustion engine or a windmill; valves, filters, piping etc. (to guide and control the system); and the actuator (e.g. a hydraulic motor or hydraulic cylinder) to drive the machinery.

Hydraulic Cylinders
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment (engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, and civil engineering.

Hydraulic Accumulator
A hydraulic accumulator is a pressure storage reservoir in which a non-compressible hydraulic fluid is held under pressure that is applied by an external source of mechanical energy. The external source can be an engine, a spring, a raised weight, or a compressed gas. An accumulator enables a hydraulic system to cope with extremes of demand using a less powerful pump, to respond more quickly to a temporary demand, and to smooth out pulsations. It is a type of energy storage device. Wherever hydraulic tasks need to be performed, hydraulic accumulators can help. They are versatile, make your machine more convenient to use, secure your hydraulic system and are used to increase the energy efficiency of hydraulic systems and for many other tasks.

Hydraulic Valves
A hydraulic valve properly directs the flow of a liquid medium, usually oil, through your hydraulic system. The direction of the oil flow is determined by the position of a spool. A hydraulic system can only function - as per requirements - by using valves. Thus, you should always look for the correct type of hydraulic valve to serve your intended purpose. The required size is determined by the maximum flow of the hydraulic system through the valve and the maximum system pressure

Hydraulic Hose-Pipe
A hydraulic hose is specifically designed to convey hydraulic fluid to or among hydraulic components, valves, actuators, and tools. It is typically flexible, often reinforced, and usually constructed with several layers of reinforcement since hydraulic systems frequently operate at high or very high pressures. Hydraulic hose is used in a variety of industrial hydraulic systems. Dimensions, performance specifications, construction options, and features are important parameters to consider when searching for hydraulic hose. Important dimensions for the selection of hydraulic hose include the inside diameter, outside diameter, and minimum bend radius. Hydraulic hose sizes are denoted by the inside and outside diameter of the hose. The inside diameter refers to the inside of the hose or liner. The outside diameter is often a nominal specification for hoses of corrugated or pleated construction. Minimum bend radius is based on a combination of acceptable hose cross-section deformation and mechanical bending limit of any reinforcement.

Hydraulic Filter & Accessories
Hydraulic filters protect your hydraulic system components from damage due to contamination of oils or other hydraulic fluid in use caused by particles. Every minute, approximately one million particles larger than 1 micron (0.001 mm or 1 μm) enter a hydraulic system. These particles can cause damage to hydraulic system components because hydraulic oil is easily contaminated. Thus maintaining a good hydraulic filtration system will increase hydraulic component lifetime.

Hydraulic Lift Block
This control blocks are designed for the complex and flexible requirements in the area of lifting technology. They are tailored solutions for lifting-lowering controls which are, depending on the control block, load-dependently, load-independently or proportionately controlled. Applications include, for example, scissor-lift platforms, small lift trucks and pallet trucks. The permissible load is secured by means of an integrated pressure relief valve. The 2/2 two-way pilot valve is equipped with manual emergency lowering with self-actuating reset. A built-in return valve prevents uncontrolled lowering. A measurement connection is provided for for easy pressure measurement. In addition, a flange connection of the block to an optionally deliverable connection plate is possible.

Hydraulic Filtration Trolleys
Hydraulic oil filtration unit is a compact, portable filter system designed to use at the site for contaminated oil. It is easily wheeled to the sump or reservoir by a single person. It is completely self-contained and requires only electrical connection for operation. Standard features of the unit include a reliable gear pump with an integral pressure relief valve to Prevent system over-pressure. The filter cartridge also gives high performance with minimum 200 beta ratio and can be changed in few minutes.

Hydraulic Powerpack
Hydraulic power packs are stand-alone devices, as opposed to a built-in power supply for hydraulic machinery. Some power packs are large, stationary units and others are more portable. They have a hydraulic reservoir, which houses the fluid, regulators that allow users to control the amount of pressure the power pack delivers to a valve, pressure supply lines and relief lines, a pump and a motor to power the pump.

Hydraulic MS Tank
The hydraulic reservoir is a container for holding the fluid required to supply the system, including a reserve to cover any losses from minor leakage and evaporation. The reservoir can be designed to provide space for fluid expansion, permit air entrained in the fluid to escape, and to help cool the fluid. Filling reservoirs to the top during servicing leaves no space for expansion. Most reservoirs are designed with the rim at the filler neck below the top of the reservoir to prevent overfilling. Some means of checking the fluid level is usually provided on a reservoir. This may be a glass or plastic sight gauge, a tube, or a dipstick. Hydraulic reservoirs are either vented to the atmosphere or closed to the atmosphere and pressurized.
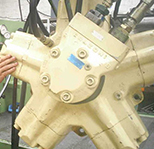
Hydraulic Motor
A hydraulic motor is a mechanical actuator that converts hydraulic pressure and flow into torque and angular displacement (rotation). The hydraulic motor is the rotary counterpart of the hydraulic cylinder as a linear actuator. Most broadly, the category of devices called hydraulic motors has sometimes included those that run on hydropower (namely, water engines and water motors) but in today's terminology the name usually refers more specifically to motors that use hydraulic fluid as part of closed hydraulic circuits in modern hydraulic machinery.
Design & Developed By Pragnyasap Copyright by @ Harish Enterprise. All Rights Reserved

 WhatsApp Us 24×7
WhatsApp Us 24×7